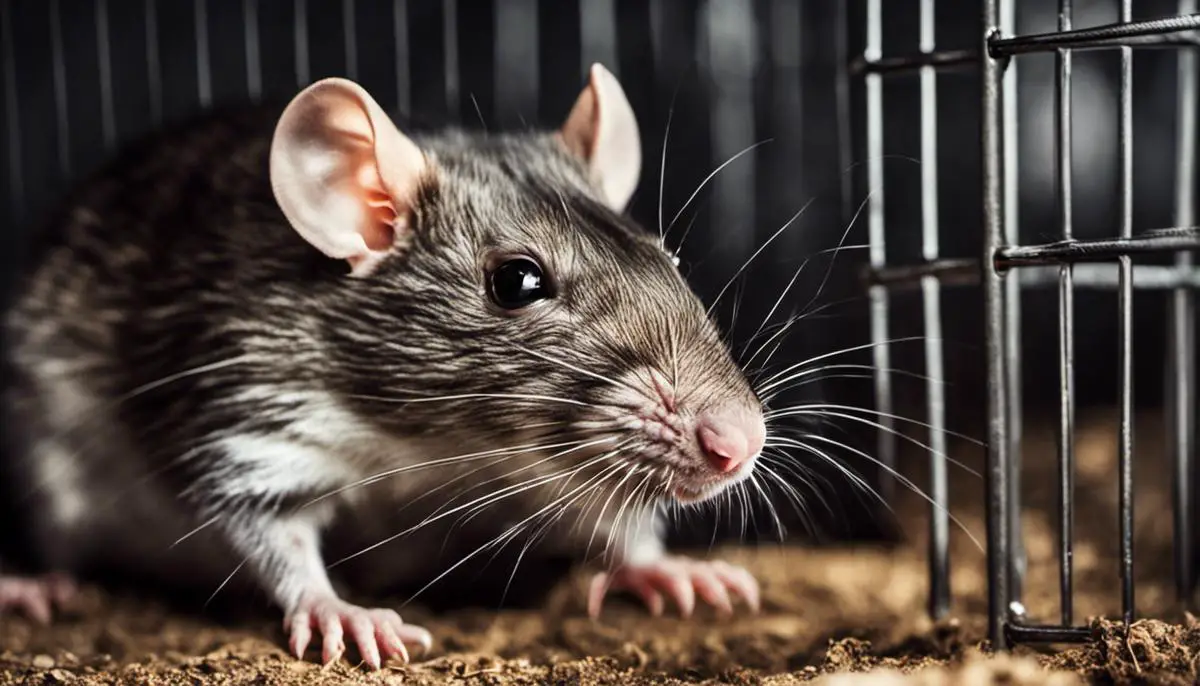
As anyone living in both urban and rural areas can attest, rats pose significant challenges due to their destructive nature and potential to spread diseases. Grasping the concept of their behaviors is the first step in devising effective rat prevention methods.
By understanding their traits, including their habitats, feeding habits, and reproductive cycles, we can outmaneuver these pesky creatures. Moreover, maintaining our surroundings using effective sanitation practices, such as proper waste management and prudent food storage, can create an environment that’s less inviting to rats. Equipping ourselves with the knowledge about different rat control methods, including sealing possible entry points and properly using rat traps and poisons, can further fortify our homes against unwanted rat infestation.
Understanding Rat Behaviors
Renowned in both scientific and lay spheres for their tenacity and adaptability, rats have managed to permeate human habitats the world over. Unbeknown to many, several nuanced behaviors lead to rat infestations and warrant meticulous understanding.
To begin with, rapid reproduction is among the most prominent causes. In favorable conditions, a female rat can produce up to 5 litters per year, each comprised of 6-12 offspring. This prolificacy allows rat populations to flourish, marking the inception of infestation if unchecked.
Nocturnal behavior is another key factor. Rats are primarily active at night, which makes their presence elusive. This ability to thrive under cover of darkness imbues them with the capacity to multiply and infest areas before any noticeable manifestations appear.
It’s largely the opportunistic diet of rats that accrues the conditions for infestation. They are omnivorous and can subsist on a myriad of food sources. Their ability to feed on both plant and animal matter, compounded with an affinity for human food and waste products, makes them thrive in urban and suburban settings.
Following the food trail, we find that rats exhibit an innate behavior called ‘hoarding’. They tend to store surplus food material, which not only allows individual rats to survive longer but also fosters comfortable conditions for population growth.
In synchrony with their opportunistic feeding pattern, rats also exhibit adaptability in their nesting habits. They can subvert an assortment of spaces, such as basements, attics, wall cavities, and ground burrows, into suitable settlements. Their propensity to find and infiltrate these diverse dwellings inadvertently accelerates the onset of infestation.
Another paramount factor lies in the rats’ social structure, where they are communal creatures by nature. They can live in large groups or ‘colonies’, overseeing complex communication and cooperation among members. Essentially, one rat’s presence often indicates others, rendering this behavior conducive to infestation.
Allied to this dynamic is ‘neophobia’, a persuasive behavior nascent in rats. The presence of new objects in their surroundings incites suspicious and cautious behavior in them, largely reducing the efficacy of newly placed traps or bait stations.
The deep-seated intrinsic behaviors of these pernicious rodents facilitate their rapid proliferation and eventual infestation. Recognizing these behaviors not only accentuates the understanding of rat biology but also underpins strategies for effective pest control. Although these creatures may induce exasperation in the homes they invade, the scientific exploration of their behaviors offers a fascinating insight into adaptability and survival in the face of adversity. Therefore, nurturing this understanding can be instrumental in devising relevant and practical measures to thwart rat infestations.

Effective Sanitation Practices
The Role of Sanitation in Thwarting Rat Infestation: Essential Strategies
A rat infestation is a matter of grave concern, posing significant health risks and structural damage. Thus, understanding the dynamics of prevention, specifically through sanitation, holds paramount significance.
Critical in rat control is the proper management of potential feeding sources, as typically, these pests are attracted to abundant food supplies. Waste management protocols should be stringent, ensuring garbage and recyclables are stored in sealed, rat-resistant containers. Notably, organic waste, emanating distinct olfactory cues, proves very appealing to rats. Hence, frequent disposal or the use of compost bins should be regular practices.
Next, sanitation extends to the maintenance of the structural integrity of buildings and surroundings. Since rats demonstrate remarkable acrobatic skills, ensuring that buildings are secure from top to bottom is essential. This includes sealing all cracks and crevices, maintaining clean and clutter-free surroundings to limit nesting sites, and managing vegetation that may provide shelter or a climbing avenue.
Cleanliness, in general, plays a pivotal role in rat infestation prevention. Regular sweeping or vacuuming can eliminate crumbs and reduce potential food sources while decluttering can reduce nesting opportunities. Since rats are known to nest in piles of clutter, such as old newspapers and boxes, discarding these items regularly can contribute to rat control.
Furthermore, part of sanitation is ensuring an environment conducive to human health. This involves regular and thorough cleaning of areas that may foster the growth of pathogens rats frequently harbor, like kitchens and bathrooms. By maintaining these areas, one also limits potential food and water sources for rats, respectively.
Rat infestations are not merely an issue of comfort and convenience; they speak to the very heart of public health and safety. Whilst they may demonstrate daunting adaptability, effective sanitation can significantly reduce their prevalence. Pursuing these sanitation strategies can help minimize the risks associated with rat infestation, ensuring a cleaner, safer environment overall.
Embracing and understanding these sanitation measures provides a gateway to mitigating the impact of these persistent pests. May all leverage this knowledge to strive towards a rat-free dwelling: a testament to the power of human adaptiveness and an essential step towards harmonious living.

Rat Control Methods
In the ongoing quest to thwart rat infestation, several techniques have stood the test of rigorous research and practical application. Beyond the realm of conventional wisdom, these proven methods have been devised by integrating the principles of engineering, biology, and environmental science.
Among the initial and perhaps the most crucial steps is the thorough sealing of homes and buildings, repelling the ingress of these persistent creatures. Attention to minute details, akin to the scrutiny one would lend to a scholarly manuscript, can make an enormous difference. Minute cracks and crevices, areas around pipework, and vent spaces must be identified and sealed using materials such as steel wool or caulk, which discourage gnawing—an innate behavior of these tenacious rodents.
Transcending beyond physical barriers, chemical deterrents function as the next line of defense. Various commercially available rodenticides have been proven potent in their ability to reduce rat populations. While effective, their employment must act in parallel with an acute awareness of their environmental impact and potential harm to non-target species.
Regular professional inspections are another potent weapon in this ongoing nutritional battle. These specialized services can detect infestations before they proliferate extensively. Employing advanced technologies, such as non-invasive thermal imaging, professionals can identify hidden nesting sites that might elude the untrained eyes.
Strategically deploying traps can also be efficacious. Snap traps and live traps provide an avenue for population control without resorting to environmentally sensitive poisons. Employing these in tandem with understanding rat behavior can drive the optimal placement and baiting of traps, hence maximizing their effect.
Beneath the umbrella of community participation lies yet another significant facet in our fight against rat infestation. The incorporation of rat control into broader community sanitation and waste management programs can enact a substantial difference, curtailing the rat populations at the ecological level.
Last, a meticulously designed and implemented integrated pest management (IPM) approach has shown promising results. The essence of IPM lies in its holistic perspective, wherein an amalgamation of prevention, observation, and intervention strategies are applied systematically to keep the rat populations in check while minimizing the use of pesticides.
In conclusion, the war against rat infestation, in its subtle interplay of environmental, biological, and structural aspects, resembles less a brute force endeavor and more a carefully choreographed dance— a testament to the study’s layered, intricate nature. The strategy must be fittingly multifaceted, perpetually adaptive, and invariably proactive.
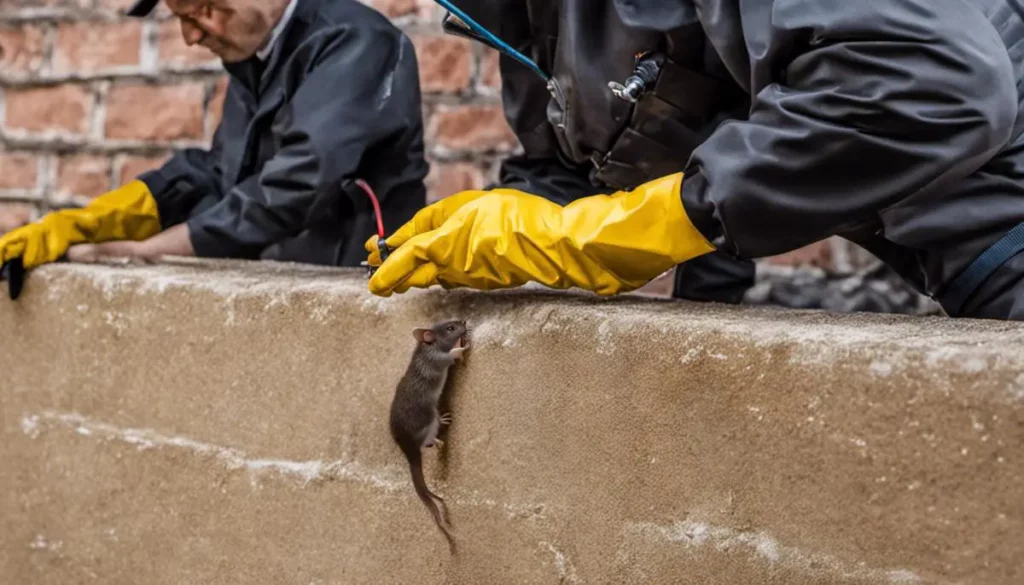

Understanding and acknowledging the behaviors and habits of rats is a fundamental component of building a comprehensive rat prevention strategy. Appropriate sanitation methods can discourage rats from making a nest in our homes, while learned control measures can give us an upper hand in managing these creatures. It’s significantly more beneficial to maintain an environment that prevents rat infestation than to control an outbreak afterward.
Remember, preventing rat infestation starts with understanding them and continues with enforcing effective sanitation practices and rat control methods. By adopting these techniques, not only can we protect our properties from damage, but we also contribute to a healthier and safer community.